|
By: Aanchal Gupta, Program Coordinator, NaRCAD Tags: Detailing Visits, CME, E-Detailing You asked, we answered! Getting your foot-in-the-door to schedule a detailing visit is a challenge for many detailers. We’ve compiled some of our best tips about gaining access from our past interviewees on the DETAILS blog.  Relationship Building:
 Incentives:
Tools:
Our team at NaRCAD recognizes the difficulties detailers face in getting the 1:1 visit, and we’re here to support you! Check out the list below for more resources on gaining access. Additional Resources on Gaining Access:
Have any additional questions or thoughts on gaining access? Write to us in the comment section below! Overview: Mary Moody joins us from the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) College of Pharmacy to discuss the passing of an 2019 act providing AD to Medicaid prescribers in Illinois state, and how AD programs with similar legislative aspirations can follow in UIC's footsteps in securing support and funding for their work. Written by: Winnie Ho, Program Coordinator Tags: CME, COVID-19, Health Policy, Opioid Safety, Program Management  Winnie: We’re very excited to have the opportunity to discuss with you regarding the efforts behind the passing of legislation in Illinois that helped cement the provision of AD services to Medicaid prescribers across the state! But before we get deeper into that, can you tell us a little bit more about yourself and your AD-related work? Mary: I’m an Associate Dean for Professional and Governmental Affairs at the UIC College of Pharmacy, in addition to a Clinical Associate Professor. I started in Drug Information and for years, was managing our Drug Information Center which supports healthcare professionals around the country. We’ve been working with the state for some time now, supporting the Medicaid prescriber population with the prior approval process. Within that timeframe, we started to look into AD to get a better understanding of how we could implement this for our providers.  W: That’s a background that certainly lends itself to promoting AD. Can you walk us through what this legislative act details? M: The bill outlines the development of a program to provide AD to Medicaid prescribing physicians. The bill also includes two specific components – one of which was an agreement to provide free CME which is available on our website, and the second of which was establishing a toll-free drug information phone number and e-mail for providers to reach out to us after their visit. We have trained drug information specialists who can answer any questions they have about medications. W: It’s important that this act received approval and support from the Illinois General Assembly. Can you talk to us about how this bill came to the floor and how it came to pass?  M: One of our legislators – Representative Theresa Mah – had attended the 2018 National Conference of State Legislators, which is an organization that acts as a percolator for new ideas about new laws. There, she learned about AD as there have been similar legislative acts established in other states, such as New York. She became really interested in bringing something similar to Illinois. In my role with Professional and Governmental Affairs, my responsibility is to keep track of proposed bills that are in the hopper, and when I saw that this bill was coming up, I was like wait, this is perfect! I set up a meeting with the representative to describe the vision and plans we had at UIC College of Pharmacy.  At this point, UIC had completed a pilot with AMITA Health to look at the benefits of AD in opioid prescribing through a CDC grant. Because of this prior experience, we were recommended to the state as a partner for this initiative. Eventually, Dr. Todd Lee and I were invited to present in front of the state House and Senate committees where we introduced AD and answered any questions the representatives had. It was ultimately passed through House and Senate unanimously. I felt pretty great about that.  W: I’m glad to hear that the legislators really prioritized this. For the world of AD, this is a major win, especially as other AD programs may be interested in replicating your success on the legislative floor. M: The legislative route is incredibly useful because it helps give me a higher level of comfort knowing that my budgeting for our AD work is likely to come on an annual basis. W: I’m curious about how you were able to introduce AD to a brand new audience and persuade all of them that this work was something they ought to prioritize.  M: Since there have been several places that have established the legislation including New York, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Maine, Massachusetts, Vermont, and Washington D.C, we were able to establish that there was precedent and could show them previous models. We were able to demonstrate how this would benefit Illinois, especially in reaching our targets of improving prescribing, reducing emergency room visits, and reducing hospitalizations for our chronically ill. We discussed how there were a large number of individuals in our state who were Medicaid recipients that suffer from multiple chronic conditions, and that it was difficult for our prescribers to stay up to date with so much information coming at them. We wanted to provide the best evidence-based, non-biased information.  W: Your program kicked-off your work by focusing on the opioid overdose crisis. How was this chosen as a starting point? M: It’s a public health crisis that is an absolute priority in Illinois. UIC has been working on research in academic detailing and the impact on opioid prescribing. We could match our pitch for AD to this current issue, it helped our presentation to the committees a lot. W: When it comes to legislation, sometimes it can require many things to align. In this case, we’re trying to align healthcare interests, research, and the policy decision-making process. There’s always a lot of competing interests and AD is certainly not the only tool in the toolkit towards improving patient outcomes.  M: For anyone looking to intertwine AD with their state legislative process, you need to understand what your state’s priorities are. You can start by looking at state plans and guidelines for major health issues, just like the opioid crisis. No one is against making these health issues better for everyone, but you may need to do more research to understand where your program fits in and more importantly, who the movers and shakers in your governance are. W: Right, these connections are critical to building support. M: One of the things that can be frustrating is not knowing where to start. You can start by talking with local universities, your state and local public health officials. There’s state pharmacy and physician organizations who may have more experience with the legislative process. Look at where your opportunities to ask for help are. Ask people for their input. You don’t have to do this all on your own.  W: Is there anything else that’s useful to prepare before choosing the legislative route? M: Having done a pilot makes a huge difference, because it shows that it can work in some part of your state. It shows that you know what might work and what won’t work. It can be hard to get a pilot done without a lot of funding, but sometimes you’ve got to use a little sweat equity, bite the bullet, and just do it. It doesn’t have to be large. You can work with a local health department to identify physicians that they have good relationships with already, or a county medical society. Having data ready is really important. W: All of this is valuable insight, thank you Mary! Although COVID-19 has interrupted some of these AD plans, what is your hope for what passing this legislation will mean for AD in Illinois?  M: Our current legislation specifically mentions supporting Medicaid providers. The goal is to expand it to all prescribers across Illinois. COVID-19 has also taught us a lot, and changed a lot of opinions on telehealth. I think as people become more comfortable with this platform, it will change how we approach AD. We’re also looking at expanding beyond physician prescribers to include Nurse Practitioners and Physician Assistants. It’s harder to get access to them. It’s an uphill battle to get names and contact information, and to know who the right providers are. But it’s important because NPs and PAs account for a large portion of prescribers for this patient population. W: I think we’ll definitely see a ripple effect, and hopefully see AD take hold more broadly. Have thoughts on our DETAILS Blog posts? You can head on over to our Discussion Forum to continue the conversation!  Mary Lynn Moody BSPharm, is the Associate Dean for Professional and Governmental Affairs and a Clinical Associate Professor in the Department of Pharmacy Practice at the University of Illinois Chicago (UIC) College of Pharmacy. Ms. Moody graduated from the University of Illinois Chicago and completed a PGY1 Residency at Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago. Ms. Moody’s clinical practice was in Drug Information at UIC. She is also currently the Director of Continuing Education at the College. In January, 2020 Mary was involved in launching the Academic Detailing Program at the college. An interview with Ellen Dancel, PharmD, MPH, Director of Clinical Materials Development, Alosa Health. Ellen completed her pharmacy practice residency at Massachusetts General Hospital and later completed her Master of Public Health at Boston University. by Anna Morgan, MPH, RN, PMP, NaRCAD Program Manager Tags: Materials Development, Detailing Visits, CME  Anna: Hi Ellen! Thanks for joining us today – we’re excited to hear about your 6+ years of experience developing impactful detailing materials. Can you walk us through the process you take when beginning to design a detailing aid? Ellen: Absolutely! The most important question to start with is, “who are you detailing with this material?” You also want to consider who is driving the goals of the intervention. Is there something your funder wants you to communicate in terms of key messages or is there new clinical information to convey? You then need to think about how to engage subject matter experts (SMEs). We work with an amazing endocrinologist for our diabetes modules and often ask, “what do you wish a primary care provider (PCP) knew before they referred a patient to you?” Having a specialist’s perception on what concerns they see in practice is key. We’re also fortunate to have access to focus groups at Alosa. We engage prescribers who receive our content to understand their needs on a topic. These peer-to-peer conversations are hosted by one of our clinicians. We also utilize our detailers’ years of expertise, gaining their insights on the materials. We use these two distinct focus groups to provide feedback on the content and messaging as well as the layout and visuals of our draft materials. We then take all this information and add it to the available literature to create a final detailing aid.  A screenshot of a cover page A screenshot of a cover page Anna: These first steps are crucial when thinking about developing materials. Let’s talk about the layout of the detailing aids. What does that look like? Ellen: When it comes to laying out the detailing aid, Alosa has a certain look and feel that we always use that’s part of our brand. The front of the document is a cover page with a title and graphic. Our graphic designer does a tremendous job of taking a concept that isn’t quite fleshed out and making sure that the end product is streamlined. A title that works well is something that is very clear, simple, and focuses on the overall message. Our team selects images for the cover page that relate to the topic but also tend to generate conversation. The back has our logos and a description of the authors. On the inside, we start with a “why do I care?” section, so we can explain why the topic we’re focusing on is of importance to the clinicians being visited. The next page is often a summary of the content that is within the detailing aid. A summary could be an algorithm for treatment or a graphic for a framework for thinking about how to approach management (e.g., the four stages of heart failure). This is followed by the evidence, data, and tips to support a PCP in order to put the key message into practice. We follow that with a cost page, so the clinicians are informed when presenting new medications to patients. Lastly, we include a reminder page that summarizes key points. 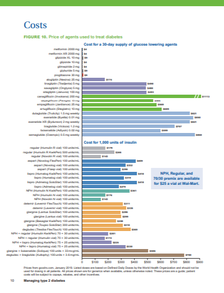 A screenshot of details on cost of medication A screenshot of details on cost of medication Anna: Wow! It’s so helpful to hear about the process your team uses for laying out content in the detailing aids at Alosa. From start to finish, how long does this entire process take? Ellen: It really depends on the topic. For example, if we’re updating a topic with a SME who has previously worked with the Alosa team, then we’d expect a timeline of around two to three months. For something new, such as a primary palliative care module or a serious illness module, we’d plan for a timeframe closer to four to six months, because we need the time to really look at the evidence and see how it shapes what we want to accomplish in the field. We also need the time to understand what our PCPs are interested in through feedback from a focus group and informally from our detailers. For AD programs with shorter timelines, we’ve found the resources at the CDC to be incredibly useful, such as the adapted patient materials for our latest immunizations module. There’s also a lot of academic detailing programs that have publicly accessible materials. Some may even allow you to use their graphics if you request permission or cite appropriately.  Anna: It’s so important to allow enough time to not only create and build a detailing aid, but also work through multiple revisions of it. Ellen: I couldn’t agree more. When I created my first detailing aid, it took me a week to even come up with the first draft, which was then subsequently torn apart. My draft looked nothing like what we ended up with at the end of the process. Programs need to plan for time for back and forth communication and to engage as many viewpoints as they can. Our modules are accredited for continuing medical education and we have reviewers assess the detail aid to ensure accuracy. We also make sure that our detailers, who will be using the material in the field, have an opportunity to try out the materials. We often end up changing key graphics that we thought were fantastic but turn out to not be effective during the detailing visit through this process. Anna: When thinking about the gold standard for creating a detailing aid that is accessible to both detailers and clinicians, what comes to mind? Ellen: It’s really a marriage of evidence-based recommendations and clinical practice. We’re trying to find a way to bridge recommendations in the literature with usable tools for a busy primary care provider’s practice. We make sure we’re providing the best and latest evidence in a way that can be helpful for the primary care provider without them having to do a complete system redesign. Materials should be streamlined and allow clinicians to be flexible in their approach by offering different options in adopting the key messages.  Anna: Thanks for walking us through this process, Ellen- what would you say are the key tips/takeaways for detailing programs who are just starting to do this? Ellen’s Tips for Creating Materials
Learn more by checking out the Alosa website, and these detailing aid building tools and examples from the NaRCAD team. Have thoughts on our DETAILS Blog posts? You can head on over to our Discussion Forum to continue the conversation!  Biography. Ellen was a pharmacist at the Massachusetts General Hospital for ten years prior to joining Alosa Health, serving in various leadership roles. She received her MPH in epidemiology from Boston University where she worked on a project looking for potential economic efficiencies in the global donor-funded antiretroviral market. As Director of Clinical Materials Development, she leads the development of evidence-based, academic materials, in partnership with clinical experts, and oversees the production of clinical content from concept to completion. An interview with Kelsey Bolton, Continuing Professional Development Consultant, Gundersen Health System by Anna Morgan, RN, BSN, MPH, NaRCAD Program Manager Tags: Detailing Visits, COVID-19, CME, E-Detailing, Smoking Cessation, Substance Use  Anna: Hi, Kelsey! Thanks for taking the time to chat with us today. Can you tell us a bit about your academic detailing program in Wisconsin and your role? Kelsey: I’m a Continuing Professional Development Consultant in the Continuing Medical Education (CME) Department at Gundersen Health System. Gundersen Health System is a teaching hospital with a multitude of specialties that serves patients in Wisconsin, Minnesota, and Iowa. As part of my CME work, academic detailing stood out as an effective tool to disseminate our information and meet our clinicians’ educational needs. We started our detailing program last fall and have been focused on tobacco cessation. The detailing intervention is a spinoff of a performance improvement project we are working on for diabetes. I’m currently a one-woman show; I’m the program coordinator and the sole detailer. I detail physicians, NPs and PAs across the health system. Anna: Wow, it’s incredible that you’ve been able to build your detailing program from the ground up! Can you tell us what that’s been like? Kelsey: Academic detailing was a new concept to me prior to being introduced to it by my former manager, who sent me to the NaRCAD training in May 2019. Academic detailing is not a well-known concept in our hospital system. It was difficult to get past the gatekeepers and “enlighten” them about academic detailing. There are still misconceptions when I walk into a room for a meeting with a clinician – they often think that I’m a drug sales rep, that I’m an internal quality control person, or that I’m there for punitive reasons. I must quickly refute that and explain that I’m there to support and unburden them, not to make judgments about their work. Anna: Those misconceptions are quite common when starting a new academic detailing program. How are you able to “enlighten” the gatekeepers? Kelsey: It was bumpy at first and we tried a few different approaches, but I think we’ve finally been able to smooth it out. I have an advantage because I’m internal and I’m contacting clinicians from an internal email or phone number. I’ve also had our medical program coordinator, the doctor who is partnering with me to learn the clinical information, send out emails to gatekeepers prior to my detailing visits. Anna: Stakeholder buy-in is imperative when building a new detailing program.  Kelsey: Absolutely. Building relationships with key stakeholders has made all the difference. The medical program coordinator I work with, as well as other experts in the organization, helped me curate my detailing aid and key messages. I practiced my detailing sessions with these stakeholders before going out in the field. It was an easy way to build relationships and get them on board – it only took a 15-minute practice detailing session! I’m also fortunate enough to have support from senior leadership. They’ve been able to open doors by letting people throughout the organization know that they support the academic detailing work I’m doing. Anna: It sounds like both managing your academic detailing program and being in the field has helped you be successful in getting your program off the ground. What has it been like to grow and manage your AD program? Kelsey: It’s like herding cats! The detailing program is 25% of my workload, so completing all the administrative work plus the detailing visits is quite a commitment. By the end of this year, I will have detailed over 200 clinicians. “Marathon detailing” has put me in a groove. It has definitely been challenging, but I appreciate that I know the ins and outs of it now – both the administrative tasks and the field work. I feel prepared to help train others. I plan to start training one of my colleagues to become a detailer in the fall. Anna: When thinking about team expansion, it’s also important to think about the impact of COVID-19. How has COVID-19 impacted your program? Kelsey: We paused our detailing visits for about 3 months, and by the time we started talking about bringing them back, NaRCAD was putting out a lot of information about e-Detailing. Before COVID, I had barely done anything with video calling, but getting thrown into working from home, we jumped into a lot of video calls. I learned how to work virtually on the fly, which made it easier to adapt to e-Detailing. I did a few practice e-Detailing sessions with my colleagues and I’ve now successfully completed several visits virtually. The NaRCAD webinars were a lifesaver. We plan to continue e-Detailing until it’s safe to return to in-person visits. Anna: A lot of academic detailing programs had to adapt quickly to e-Detailing during the pandemic. What does the future look like for your program?  Kelsey: For the more near future, we are working on collecting data for the tobacco cessation campaign to eventually publish research on the efficacy of the academic detailing intervention. We’re going to pull patient data from the EMR, as well as look at the qualitative data from the evaluation surveys. This research will help inform our organization on the benefits of academic detailing as an educational intervention. We would also like to continue the program with other strategic initiatives like substance use disorder, social determinants of health, and cancer screening. I have a soft spot for topics similar to tobacco cessation that are sometimes discouraging to clinicians because they don’t feel like they can make a difference. I know that through detailing, I’m able to give them a fresh take on these topics, and reinvigorate them in providing the best care for their patients. Have thoughts on our DETAILS Blog posts? You can head on over to our Discussion Forum to continue the conversation!  Biography. Kelsey Bolton is a Continuing Professional Development Consultant in the CME department at Gundersen Health System in La Crosse, WI and the program lead for its Academic Detailing program. She received her Bachelor of Arts degree in Communication Studies in 2015, Healthcare CPD Certificate in 2019, and is currently pursuing her Master’s in Organizational Leadership. She has completed over 100 detailing visits and is presently conducting a research project on the efficacy of tobacco cessation academic detailing.  Tags: Autism, CME, Conference, Detailing Visits, Pediatrics, Practice Facilitation, Training NaRCAD: Hi, Meagan and Mindy—thanks for taking the time to talk with us about your clinical outreach education programming at Colorado ABCD. Can you give us an overview about ABCD and its mission to improve child development? Meagan Shallcross: Colorado Assuring Better Child Health & Development (ABCD) works with community partners, pediatric healthcare providers, early learning providers, and families across Colorado communities. The goal is to strengthen systems and identify children with developmental delays, connecting them with community services as early as possible.
 Meagan Shallcross, MPH Meagan Shallcross, MPH NaRCAD: Tell us a bit about your backgrounds. How did you each get into healthcare improvement? Meagan: My background in public health, along with experience working in clinical settings and behavioral science research, developed my interest in healthcare improvement that aims to bridge community work and clinical practice, standardize clinical workflows, and ultimately improve experiences and outcomes for patients and families  Mindy Craig, PA-C, M.S. Mindy Craig, PA-C, M.S. Mindy Craig: My path to healthcare improvement is a little different than what you might expect. I worked for Northwest Airlines as a flight attendant for several years straight out of college. At that time the airline industry was losing a large amount of money and needed to find a new way of operating. They decided to utilize a Total Quality Management approach and enlisted people from every department to undergo training in TQM and then facilitate small departmental groups in quality efforts. It was through this process that I began to understand the importance of doing business with a quality framework.  Learn more at coloradoabcd.org. Learn more at coloradoabcd.org. Eventually, I left Northwest and started working in a Neurology clinic while going back to school with the goal of becoming a PA. After completing my degree I worked in primary care settings for about 10 years. I participated in small clinic QI efforts over the years and continued to be interested in quality improvement. I was hired by ABCD 8 years ago to bring a clinical perspective to their physician outreach. It was a natural progression for me to start approaching our work at ABCD with a quality improvement framework. The power of engaging front line staff to implement changes that result in improvement remains as strong as it was when I worked in the airline industry. NaRCAD: Talk with us about your academic detailing programming at ABCD—you’ve been doing this for about 10 years, right? Mindy: We started our work encouraging the use of standardized developmental screening tools in the primary care settings. This was supported by the American Academy of Pediatrics policy statement in 2006 recommending the use of these tools at well child visits. We offered informal outreach to physicians providing instructions on screening tools, billing information, AAP recommendations and information on referral resources. We quickly recognized that screening alone wasn’t sufficient and began talking about the referral process and how to ensure successful referrals were being made. At around this time, research was showing us that only about 50% of children referred for Early Intervention services were actually connecting to that referral. It was easy to identify children with concerns but not as easy to ensure they received needed support. We decided to try formalizing our approach to outreach by offering Continuing Medical Education [CME] credits. While we didn’t change content, offering CME changed the way providers saw us as detailers. We appreciated the new credibility, but still struggled with recruiting new practices. NaRCAD: Recruiting practices to participate is a challenge for many programs. How did this struggle transform into quality improvement?
We now offer Quality Improvement [QI] and MOC projects for implementing developmental screening, autism screening and postpartum depression screening in addition to a project that aims to increase the percentage of children who successfully connect with Early Intervention when referred from their primary care provider. We have been thrilled with the response from physicians for participating in these projects and just received funding to continue and grow our outreach efforts. NaRCAD: What have been some other challenges you’ve faced when going in to talk to clinicians about implementing developmental screening? Mindy: I started working at ABCD unsure of how to provide physician outreach, so I naturally modeled my efforts on the one successful approach I knew very well, which was pharmaceutical sales. As the recipient of pharmaceutical detailing, it was pretty easy to begin my outreach efforts in a similar fashion. I quickly learned how it feels to be a detailer. Front office staff rejected me repeatedly, I made hundreds of phone calls that didn’t get returned, and when I did get to speak to a provider I had to speak quickly and to the point to keep their attention. The challenge of gaining access was the biggest barrier I confronted early on and remains at the top of the list.
 A key challenge: gaining access to clinicians. A key challenge: gaining access to clinicians. NaRCAD: When dealing with those challenges, what’s helped you to build relationships with clinicians in order to gain commitment? Meagan: To deal with the challenges that arise, we have found that it helps to get creative in our approach to gain access to clinicians and add credibility to our messages. A barrier we have encountered when trying to schedule times to meet with clinicians is the expectation that we will provide food. Our funders and budgets do not allow us to pay for food, so we have opted to provide other incentives for clinicians, such as CME or MOC credit. Not only is offering CME/MOC credits an educational incentive for providers, but it lends credibility to our messages. We facilitate our QI projects through multiple meetings at the practice and have found that, by developing relationships and a presence in the office, we can overcome clinicians’ resistance to implementing screening or other changes in their practice.
 Resource and best practices exchange at #NaRCAD2015 Resource and best practices exchange at #NaRCAD2015 NaRCAD: We were happy to see you at our 3rd International Conference on Academic Detailing here in Boston a few months ago. Tell us more about how the conference helped you think about your work in a different way. Mindy: We were thrilled to be able to attend the conference and came away very energized. We highly recommend the conference to anyone doing similar work. Some of our key “take-aways” were around the fundamentals of academic detailing, including the need for profession materials and repeated visits to develop relationships. We came home committed to find money for developing professional materials and to attend the two-day intensive training offered by NaRCAD.
However, I’ve struggled with our role as a non-profit in meeting these needs. Up to this point, ABCD has utilized a very hands-on approach. We plan meetings, take notes, write up PDSA cycles, make “To Do” lists – anything we can do to make the process easy for the practice and allow the providers to concentrate on patient care. A true practice facilitation model is more concerned with increasing the capacity of the practice to continue quality improvement work after the facilitation had ended. The goal isn’t to do all the work, but to help the practice find capacity to do it themselves. NaRCAD: What other advice would give to a new and emerging AD program that’s just getting started, or that you’d give yourself if you could go back in time 10 years? Meagan: We have found NaRCAD’s training and tips to be very helpful, so we would recommend that new clinical educators attend a NaRCAD techniques training to hone their skills in communicating their messages with clinicians and gaining commitment to behavior change. One of our main takeaways from the NaRCAD conference was the importance of high-quality, professional materials, so we would recommend that new programs budget for the development of professional materials as well as food, which can be an incentive when setting up meetings with clinicians. Over the years, we’ve realized how critical it is to work with community partners before going into healthcare practices to ensure that clinical workflows, such as processes for making referrals to external agencies, are aligned with community-defined processes and so that clinicians are aware of the resources available to patients and families in their communities. NaRCAD: Thanks so much for sharing important insights from your program to improve childhood health outcomes. We look forward to seeing you at a future training and hearing more about your program's future successes! BiographiesMindy Craig, PA-C, M.S., Director of Physician Outreach, has been with the ABCD team for 8 years and brings with her experience in the clinical setting. She earned her physician assistant degree at the University of Colorado Health Science Center’s Child Health Associate/Physician Assistant program in May 2000. Concurrently, she completed additional course work and research to earn her Master of Science degree in Pediatrics. Ms. Craig worked as a physician assistant in a number of settings for ten years prior to joining the ABCD team. Her medical career has included a variety of medical office positions from medical records clerk to practice manager. This range of experience positions her to fully understand the unique dynamics and flow in a typical office, which allows her to deliver technical assistance to practices at a meaningful level.
Ms. Craig’s quality improvement experience began in the business sector where she was extensively trained on Total Quality Management (TQM) at Northwest Airlines. She worked at the airline as a facilitator, training inflight and ground personnel in the principles of quality improvement. This experience with quality continued in the clinical setting, as she has participated in and/or chaired a number of quality improvement projects over her career as a physician assistant. In addition to her work at ABCD, Ms. Craig also does consulting work for organizations needing assistance with physician outreach and education. Meagan Shallcross, MPH, Healthy Steps/Physician Outreach Coordinator, joined the ABCD team in June 2015 as the Healthy Steps and Physician Outreach Coordinator. Meagan is passionate about building systems and environments that support children’s healthy development through clinical-community partnerships and integrated care delivery approaches. Meagan earned a Master of Public Health degree at the University of Michigan, where she supported Patient and Family Centered Care projects at the university health system and was involved with community-based participatory research addressing health equity, as well as research focused on provider-patient communication. Learn more at www.coloradoabcd.org. All photos used with permission. |
Highlighting Best PracticesWe highlight what's working in clinical education through interviews, features, event recaps, and guest blogs, offering clinical educators the chance to share successes and lessons learned from around the country & beyond. Search Archives
|
