|
By Anna Morgan-Barsamian, MPH, RN, PMP, Senior Manager, Training & Education, NaRCAD An interview with Meghan Breckling, PharmD, BCACP, Ambulatory Care Pharmacist and Academic Detailer, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences and Arkansas Department of Health. Tags: Detailing Visits, Opioid Safety, Harm Reduction, Evidence-Based Medicine 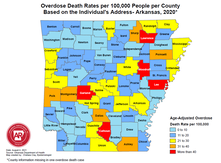 Overdose Deaths Rates per 100,000 people per County, Arkansas 2020 Overdose Deaths Rates per 100,000 people per County, Arkansas 2020 Anna: Hi, Meghan. Thanks for joining me on DETAILS today! Your team has done extensive work on pain management detailing, and you recently completed a pilot project on harm reduction in collaboration with the National Association of County and City Health Officials (NACCHO). Can you tell me a little more about this project? Meghan: Thanks for having me! We decided to target rural counties in Arkansas that have both high drug overdose deaths and naloxone administration rates. We previously created broad pain management materials for our other opioid safety detailing projects; this project took those materials to the next level. We looked at how we could better support clinicians in caring for their patients with substance use disorder (SUD) through a harm reduction lens. We provided clinicians with screening tools to help identify patients with mental health conditions and SUD to determine who could benefit from additional services. We even created a local resource guide for clinicians to easily connect patients to community services. The clinicians found that these accessible tools helped them have open conversations with patients.  Anna: I can imagine having something tangible to give to patients makes clinicians feel more equipped to have these conversations. What other resources were you able to share with clinicians? Meghan: We encouraged clinicians to utilize a new, free mental health resource called AR ConnectNow. This program provides immediate virtual care to all Arkansans dealing with mental health and substance use disorders. Clinicians were grateful for AR ConnectNow because mental health services are scarce in rural Arkansas; they’ve been sharing it with their patients frequently. Anna: You must have been proud to be part of a project that had such an impact on both patients and clinicians. How did the harm reduction lens inform your detailing visits for this project compared to your prior pain management-focused visits? Meghan: Many visits centered on communication with patients. Communication and empathy are two huge pieces to consider with this topic. We spent a lot of time asking clinicians about the conversations they have with patients and the types of questions they ask about substance use. We really wanted to understand what was going well and where there were gaps that we could help fill with resources and support. We also focused on naloxone prescribing and administration. We gave out free naloxone kits to all clinicians that they could either keep in the clinic or give to a patient who was having trouble accessing it. Clinicians were open to the idea of prescribing naloxone to patients who were at risk of overdose and open to keeping kits in their clinic in the event of an overdose. Our team had a lot of clinicians say during follow up visits that they felt more comfortable prescribing naloxone and were prescribing it more to patients and family members.  Anna: It’s impressive how you were able to clearly shift your focus from opioid prescribing to harm reduction and prioritize the relationship between the clinician and patient. Did you receive any pushback from clinicians on harm reduction? Meghan: Clinicians understood the need for harm reduction services but were more inclined to refer patients out rather than providing services within their clinics. For example, we found that a lot of clinicians were resistant to prescribing Medications for Opioid Use Disorder (MOUD), either because they were uncomfortable with the steps to do so, or they were told by leadership that they should not prescribe MOUD at their practice. It can sometimes take an hour or more for patients in rural areas to access specialty services that offer MOUD. We’re looking at future projects where we can utilize pharmacists to increase MOUD prescribing in partnership with primary care providers. For instance, a primary care clinician could diagnose SUD and prescribe MOUD, while a pharmacist could monitor the patient throughout treatment. It would take a lot of burden off the clinicians and could possibly make them less resistant to prescribing it.  Anna: Using pharmacists as an integral part of the care team is an excellent idea – you’ll have to let us know if you receive additional funding for this work! Let’s wrap up with a final question. If another program decided to do a detailing project on harm reduction, what advice would you give them before they went out into the field? Meghan: You need to take a step back and remember that there isn’t going to be instant behavior change among clinicians. For a topic this complex, it’s critical to have follow-up visits and continue to be a resource and support for clinicians. Also, be understanding of clinicians and their experiences. They’re dealing with a lot and it’s not easy to change things all at once. Building a relationship and getting a clinician to commit to just one key message is a huge win. Want to learn more? Read about the harm reduction key messages used for this project and the development of those messages on our previous blog post. Have thoughts on our DETAILS Blog posts? You can head on over to our Discussion Forum to continue the conversation!  Biography. Dr. Meghan Breckling is an Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Specialist at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS) and is a trained Academic Detailer through the National Resource Center for Academic Detailing (NARCAD) within the Center for Health Services Research (CHSR) at UAMS’ Psychiatric Research Institute (PRI). She previously completed a PGY1 Pharmacy Residency and PGY2 Ambulatory Care Residency at the Central Arkansas Veterans Healthcare System (CAVHS). Currently, she is a part of a multidisciplinary academic detailing team comprised of a pharmacist, physician and physical therapist that provide evidence-based solutions, tools and support for chronic pain management to primary care providers across the state of Arkansas. Comments are closed.
|
Highlighting Best PracticesWe highlight what's working in clinical education through interviews, features, event recaps, and guest blogs, offering clinical educators the chance to share successes and lessons learned from around the country & beyond. Search Archives
|
