 Jerry Avorn, MD, Co-Director, NaRCAD Tags: Detailing Visits, Evidence-Based Medicine, Health Policy, Jerry Avorn, Medications, Opioid Safety Of all the medication use issues facing the U.S., the most pressing is of course that of opioid mis-prescribing. When the anatomy of that mis-use is dissected, it becomes clear that the principles and methods of academic detailing are especially well suited to addressing this crisis, for several reasons.  First is the problem of information deficit: before the mid- to late-1990s, practical issues of the assessment and management of pain were often poorly covered (or not at all) in most medical school or residency training programs – so there’s a lot of good that can be accomplished by simple personalized knowledge transfer, to start with. Second is dealing with the contamination of dis-information: the growing documentation of the fact that sales reps for OxyContin, for example, actually under-stated the drug’s risks and over-stated its potential indications when describing their product to prescribers – distortions for which the company had to pay $600 million in penalties. Third is the fact that for this therapeutic category more than for most others, a prescriber’s attitudes and motivations play an especially important role. These can involve “non-scientific” issues such as:
 There is ample evidence that simple “gotcha” letters accusing a prescriber of opioid over-use have no effect. Similarly, draconian restrictions imposed by governments or health care systems limiting the amount of opioid that can be prescribed to a given patient clearly run the risk of under-treating genuine pain – a grotesque example of health care rules that seem guaranteed to increase patients’ suffering. Evidence-based guidelines, such as those promulgated by the CDC, are fine as far as they go, but most doctors haven’t read them, and even fewer have integrated them into their practices.  But a well-trained, skilled academic detailer can interact with a prescriber to understand just what issues lie behind the apparent misuse of opioids by that physician, and present a set of interactive messages tailored to those particular needs. This will involve constructing a personalized blend of new knowledge transfer, dis-information detoxification, practice facilitation (including help accessing Prescription Drug Monitoring Program data less burdensomely), accessing local resources for help in patients with opioid use disorder, and assistance with patient education. 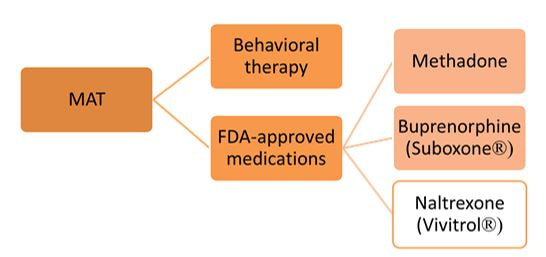 A similar approach could also be enormously helpful for encouraging naloxone prescribing and improving the care of patients with opioid use disorder, including medication-assisted treatment, where information deficits and attitudinal issues are even more prominent. Together, this kind of individualized outreach education can accomplish far more than mailed guidelines, accusatory nastygrams, or legal restrictions – and in doing so, do more to improve patient care and reduce preventable misery than can be expected from more old-fashioned interventions.  Biography. Jerry Avorn, MD, Co-Director, NaRCAD Dr. Avorn is Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School and Chief of the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics (DoPE) at Brigham & Women's Hospital. A general internist and drug epidemiologist, he pioneered the concept of academic detailing and is recognized internationally as a leading expert on this topic and on optimal medication use. Read more. Comments are closed.
|
Highlighting Best PracticesWe highlight what's working in clinical education through interviews, features, event recaps, and guest blogs, offering clinical educators the chance to share successes and lessons learned from around the country & beyond. Search Archives
|
